Share a Free SSL Certificate Application/Renewal and Automatic Deployment Website - httpsok, one command, easily handle SSL certificate auto-renewal and deployment.
The certificate application supports wildcard domains, with certificate issuers including ZeroSSL, Let's Encrypt, and Google.
Automatic deployment supports: nginx (provides a one-click script for automatically applying SSL certificates and deploying), Qiniu Cloud, Tencent Cloud, Aliyun, Volcano Engine, Huawei Cloud, Baidu Intelligent Cloud, Wangsu, Baishan Cloud, Dogecoin Cloud, LB (Load Balancer).
API support for automatically updating certificates to various CDN/OSS providers!
httpsok Website Address (Including AFF): https://httpsok.com/p/4ywD
Free version quota: 5 wildcard certificates, 50 automatic deployments (WeChat scan for registration; if you have multiple WeChat accounts, you can register multiple accounts to get free access. Paid options are also affordable, starting at just 29 CNY/year). AFF invite new registered users to get additional free wildcard certificate quotas.
There’s another free certificate application site OHTTPS with automatic deployment (including AFF): https://www.ohttps.com?invitationCode=g6vy5rwd5ov82937
OHTTPS offers 1000 balance for free when you use the above AFF link (1 RMB = 100 OHTTPS balance), which can be used to purchase paid certificates.
Highly cost-effective and cheap VPS/Cloud Server recommendations: https://blog.zeruns.tech/archives/383.html
Webmaster QQ Group: 767557452
What is an SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate, full name Secure Sockets Layer certificate, is a protocol used for network communication encryption, designed to secure data transmission over the internet. SSL certificates establish an encrypted channel between the client (such as a browser) and the server to ensure data is not intercepted or altered during transmission.
Main Functions of an SSL Certificate:
- Data Encryption: SSL certificates use high-strength encryption algorithms to ensure that transmitted data cannot be intercepted or decoded by third parties on the internet.
- Identity Verification: SSL certificates can verify the authenticity of a website, preventing phishing and man-in-the-middle attacks. When users visit a website with an SSL certificate, the certificate displays ownership details, including the company name and geographic location.
- Data Integrity: SSL certificates ensure that data is not altered during transmission, maintaining its integrity.
- Build Trust: For online transactions and sensitive information transmission, SSL certificates are essential. They increase users' trust in the website because users know their information is secure.
- Search Engine Optimization: Some search engines, such as Google, prioritize indexing and ranking websites that use SSL certificates, as they are considered more secure.
- Legal Compliance: In some industries, such as finance and healthcare, using SSL certificates is a legal requirement to protect clients' privacy and sensitive information.
Types of SSL Certificates:
- Domain Validation (DV) Certificates: The most basic type of SSL certificate, which only validates domain ownership. They are issued quickly and are relatively inexpensive.
- Organization Validation (OV) Certificates: In addition to validating domain ownership, these certificates also verify the identity of the organization applying for the certificate, providing a higher level of trust.
- Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: The highest level of SSL certificate, which requires more rigorous validation processes, including verifying the legitimacy of the organization, its operations, and ownership. EV certificates display a green address bar in browsers with the organization’s name, offering the highest level of trust.
Application and Deployment of SSL Certificates:
To apply for an SSL certificate, users generally need to go through a Certificate Authority (CA). Several free and paid CAs provide SSL certificates, such as Let's Encrypt and GlobalSign. The application process typically involves validating domain ownership and (for OV and EV certificates) the organization's identity.
Deploying an SSL certificate involves installing the certificate files on the server and configuring server software (such as Apache or Nginx) to use the SSL/TLS protocol for encrypting data transmission.
By using SSL certificates, website administrators can ensure their websites are secure, protect user data, and increase user trust in the site.
Usage Tutorial

To apply for a certificate, just enter the domain name and follow the instructions to set up domain resolution. The certificate will be issued, and it will automatically renew a few days before expiration.
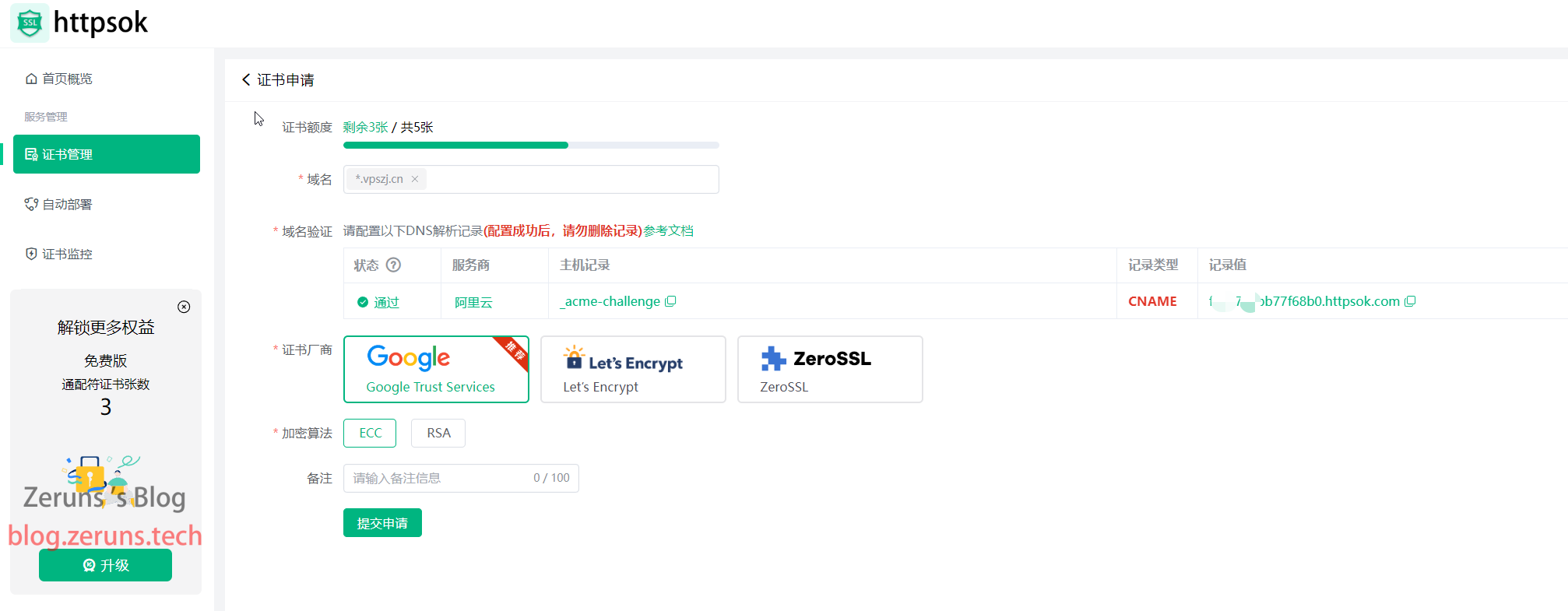

If you want to automatically deploy to a CDN, click to create a new deployment task, select your CDN provider, and follow the prompts to input your information.


It also provides free certificate monitoring services.

Recommended Reading
- Highly cost-effective and cheap VPS/Cloud Server recommendations: https://blog.vpszj.cn/archives/41.html
- Linux Email Server Setup Tutorial: https://blog.zeruns.tech/archives/822.html
- My Website was Attacked by CC again, a record: https://blog.zeruns.tech/archives/819.html
- Minecraft Server Setup Tutorial: https://blog.zeruns.tech/tag/mc/
- Linux Setup Discuz Forum Website, Website Setup Tutorial: https://blog.zeruns.tech/archives/681.html
- MechRevolution iMini Pro820 Mini Host Review and Tear Down: https://blog.zeruns.tech/archives/813.html
Source Article URL:https://blog.zeruns.tech/archives/824.html




Comment Section