Recently, I purchased an LCR bridge and decided to measure and compare the parameters of various capacitors and inductors I have on hand.
The testing equipment used is the Zhongchuang ET4410 benchtop LCR digital bridge. The measured parameters include: capacitance, inductance, D (dissipation factor), Q (quality factor), ESR (equivalent series resistance), and X (reactance, typically represented as inductive reactance XL or capacitive reactance XC).
Complete Excel spreadsheet download link: https://www.123pan.com/s/2Y9Djv-pJcvH.html
Zhongchuang ET4410 Benchtop LCR Digital Bridge Simple Unboxing Review: https://blog.zeruns.com/archives/763.html
RIGOL DHO914S Oscilloscope Simple Unboxing Review: https://blog.zeruns.com/archives/764.html
Electronics/Microcontroller Technology Exchange Group: 2169025065
Some of the capacitors tested are shown below:

Inductors
In the table below, the frequency indicates the test frequency set on the bridge. Each component was tested at four frequency points: 100Hz, 1kHz, 10kHz, and 100kHz, with a uniform test level of 1V.
Generally, a higher Q value is preferable, while lower ESR and X values are desirable.
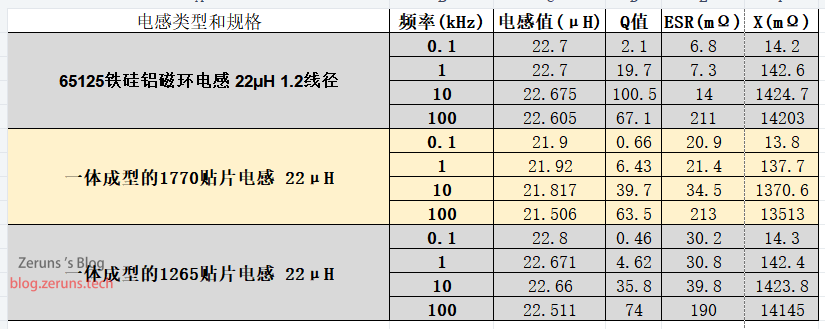
| Inductor Type and Specification | Frequency (kHz) | Inductance (μH) | Q Value | ESR (mΩ) | X (mΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65125 Iron-Silicon-Aluminum Toroidal Inductor 22μH 1.2mm Wire Diameter | 0.1 | 22.7 | 2.1 | 6.8 | 14.2 |
| 65125 Iron-Silicon-Aluminum Toroidal Inductor 22μH 1.2mm Wire Diameter | 1 | 22.7 | 19.7 | 7.3 | 142.6 |
| 65125 Iron-Silicon-Aluminum Toroidal Inductor 22μH 1.2mm Wire Diameter | 10 | 22.675 | 100.5 | 14 | 1424.7 |
| 65125 Iron-Silicon-Aluminum Toroidal Inductor 22μH 1.2mm Wire Diameter | 100 | 22.605 | 67.1 | 211 | 14203 |
| Integrated 1770 SMD Inductor 22μH | 0.1 | 21.9 | 0.66 | 20.9 | 13.8 |
| Integrated 1770 SMD Inductor 22μH | 1 | 21.92 | 6.43 | 21.4 | 137.7 |
| Integrated 1770 SMD Inductor 22μH | 10 | 21.817 | 39.7 | 34.5 | 1370.6 |
| Integrated 1770 SMD Inductor 22μH | 100 | 21.506 | 63.5 | 213 | 13513 |
| Integrated 1265 SMD Inductor 22μH | 0.1 | 22.8 | 0.46 | 30.2 | 14.3 |
| Integrated 1265 SMD Inductor 22μH | 1 | 22.671 | 4.62 | 30.8 | 142.4 |
| Integrated 1265 SMD Inductor 22μH | 10 | 22.66 | 35.8 | 39.8 | 1423.8 |
| Integrated 1265 SMD Inductor 22μH | 100 | 22.511 | 74 | 190 | 14145 |
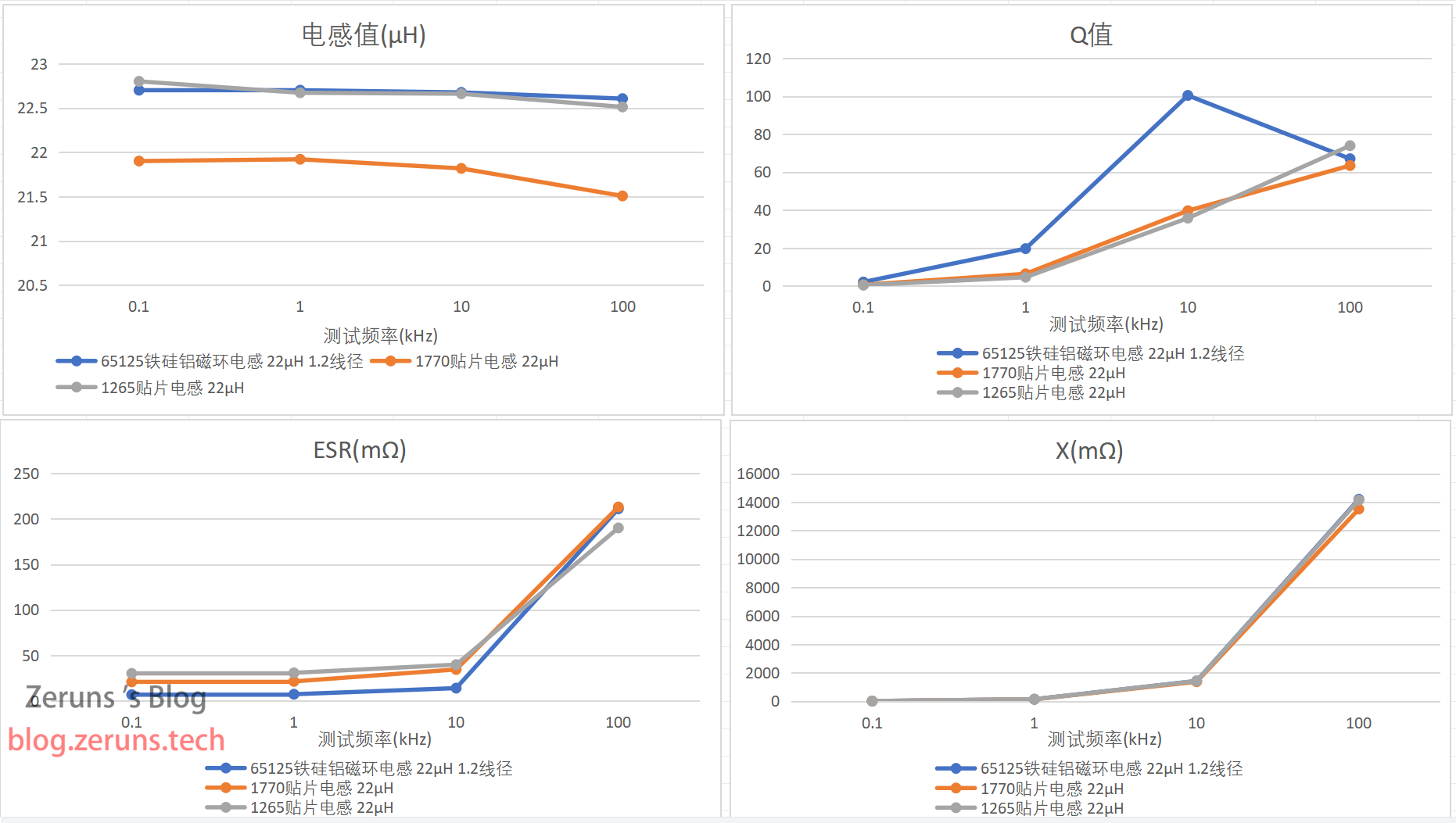
In summary:
- The high-frequency performance of the iron-silicon-aluminum toroidal inductor seems subpar; the Q value decreases at 100kHz, with the highest Q value observed at 10kHz (I also tested at 20kHz, where it was slightly higher; it appears there's a peak between 20kHz and 100kHz, after which it gradually declines).
- The integrated SMD inductors exhibit better high-frequency performance; as the frequency increases, the Q value continues to rise, surpassing that of the iron-silicon-aluminum toroidal inductor at 100kHz.
- The ESR value is lower in the iron-silicon-aluminum toroidal inductor, possibly due to the larger wire diameter; however, as the frequency increases, the ESR becomes higher than that of the integrated SMD inductors.
Capacitors
The frequency in the table below refers to the test frequency set by the impedance bridge. Each component was tested at four frequency points: 100Hz, 1kHz, 10kHz, and 100kHz. The test level was uniformly set to 1V.
Generally speaking, lower D value, ESR, and X are better.
The Rubycon and ELNA capacitors in the table were purchased from a small store on Taobao, and there is a high probability that they are counterfeit.
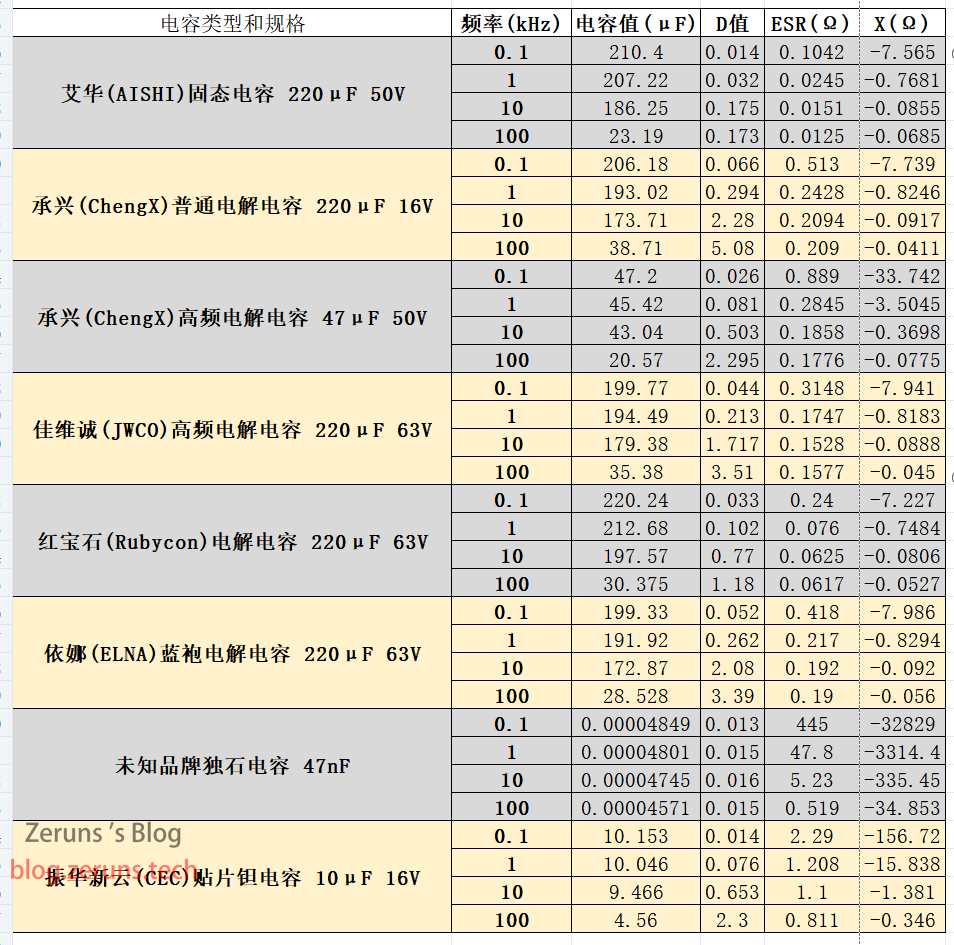
| Capacitor Type and Specification | Frequency (kHz) | Capacitance (μF) | D Value | ESR (Ω) | X (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISHI Solid Capacitor 220μF 50V | 0.1 | 210.4 | 0.0138 | 0.1042 | -7.565 |
| AISHI Solid Capacitor 220μF 50V | 1 | 207.22 | 0.0318 | 0.0245 | -0.7681 |
| AISHI Solid Capacitor 220μF 50V | 10 | 186.25 | 0.175 | 0.0151 | -0.0855 |
| AISHI Solid Capacitor 220μF 50V | 100 | 23.19 | 0.173 | 0.0125 | -0.0685 |
| ChengX Ordinary Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 16V | 0.1 | 206.18 | 0.0662 | 0.513 | -7.739 |
| ChengX Ordinary Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 16V | 1 | 193.02 | 0.2939 | 0.2428 | -0.8246 |
| ChengX Ordinary Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 16V | 10 | 173.71 | 2.28 | 0.2094 | -0.0917 |
| ChengX Ordinary Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 16V | 100 | 38.71 | 5.08 | 0.209 | -0.0411 |
| ChengX High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 47μF 50V | 0.1 | 47.2 | 0.0264 | 0.889 | -33.742 |
| ChengX High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 47μF 50V | 1 | 45.42 | 0.0811 | 0.2845 | -3.5045 |
| ChengX High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 47μF 50V | 10 | 43.04 | 0.503 | 0.1858 | -0.3698 |
| ChengX High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 47μF 50V | 100 | 20.57 | 2.295 | 0.1776 | -0.0775 |
| JWCO High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 0.1 | 199.77 | 0.0437 | 0.3148 | -7.941 |
| JWCO High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 1 | 194.49 | 0.2133 | 0.1747 | -0.8183 |
| JWCO High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 10 | 179.38 | 1.717 | 0.1528 | -0.0888 |
| JWCO High-Frequency Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 100 | 35.38 | 3.51 | 0.1577 | -0.045 |
| Rubycon Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 0.1 | 220.24 | 0.0332 | 0.24 | -7.227 |
| Rubycon Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 1 | 212.68 | 0.1018 | 0.076 | -0.7484 |
| Rubycon Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 10 | 197.57 | 0.77 | 0.0625 | -0.0806 |
| Rubycon Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 100 | 30.375 | 1.18 | 0.0617 | -0.0527 |
| ELNA Blue Robe Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 0.1 | 199.33 | 0.0523 | 0.418 | -7.986 |
| ELNA Blue Robe Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 1 | 191.92 | 0.262 | 0.217 | -0.8294 |
| ELNA Blue Robe Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 10 | 172.87 | 2.08 | 0.192 | -0.092 |
| ELNA Blue Robe Electrolytic Capacitor 220μF 63V | 100 | 28.528 | 3.39 | 0.19 | -0.056 |
| Unknown Brand Monolithic Capacitor 47nF | 0.1 | 0.00004849 | 0.0134 | 445 | -32829 |
| Unknown Brand Monolithic Capacitor 47nF | 1 | 0.00004801 | 0.0145 | 47.8 | -3314.4 |
| Unknown Brand Monolithic Capacitor 47nF | 10 | 0.00004745 | 0.0155 | 5.23 | -335.45 |
| Unknown Brand Monolithic Capacitor 47nF | 100 | 0.00004571 | 0.0151 | 0.519 | -34.853 |
| CEC SMD Tantalum Capacitor 10μF 16V | 0.1 | 10.153 | 0.0143 | 2.29 | -156.72 |
| CEC SMD Tantalum Capacitor 10μF 16V | 1 | 10.046 | 0.0763 | 1.208 | -15.838 |
| CEC SMD Tantalum Capacitor 10μF 16V | 10 | 9.466 | 0.653 | 1.1 | -1.381 |
| CEC SMD Tantalum Capacitor 10μF 16V | 100 | 4.56 | 2.3 | 0.811 | -0.346 |
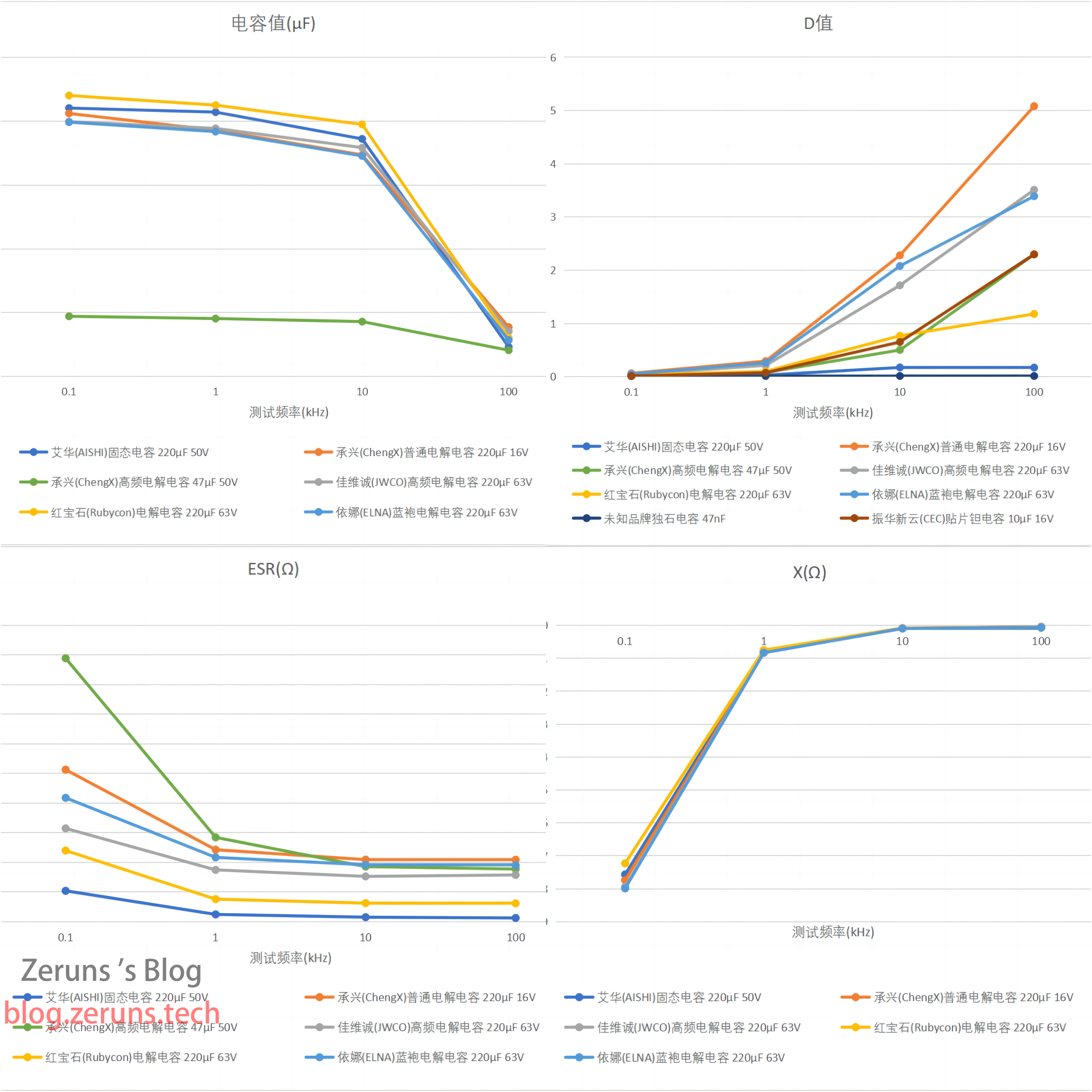
Summary:
- Solid capacitors and electrolytic capacitors show a significant decrease in capacitance after 10kHz.
- Monolithic capacitors have very high reactance and ESR at low frequencies.
- The D value of electrolytic capacitors increases significantly at higher frequencies, while solid capacitors do not change much. Solid capacitors have much better performance than electrolytic capacitors.
- There are also significant performance differences between different brands of electrolytic capacitors. Among the tested electrolytic capacitors, Rubycon has the best performance.
- The reactance of capacitors decreases with increasing frequency.
The summary may not be accurate and is for reference only.
Recommended Reading
- Highly Cost-Effective and Affordable VPS/Cloud Server Recommendations:https://blog.zeruns.com/archives/383.html
- Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Typecho Personal Blog Website on a Cloud Server:https://blog.zeruns.com/archives/749.html
- Minecraft Server Setup Guide:https://blog.zeruns.com/tag/mc/
- PalWorld Server Setup Guide:https://blog.zeruns.com/tag/PalWorld/
- Simple Unboxing Review of Ruideng RD6012P Programmable Adjustable Power Supply (60V 12A DC Power Supply):https://blog.zeruns.com/archives/740.html
- Unboxing Experience of TuoZhu A1 Combo 3D Printer:https://blog.zeruns.com/archives/754.html




Comment Section